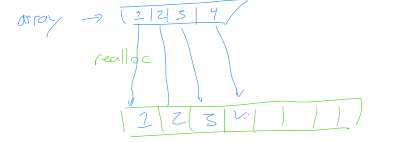
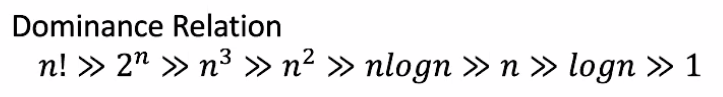SIMILARITIES AND DIFFERENCES FROM PYTHON
Similarities
- imperative languages
- range of arithmetic and logical operations
- range of control structures
- eg. selection, iteration, recursion
- function arguments are received as initial values of local variables
- libraries are available for a wide range of other operations
Differences
| C | Python |
|---|---|
| program structure indicated by semicolons and braces | program structure by layout |
| integer arithmetic is bounded; silently overflows | |
| no bool type; uses int | has bool type |
| static typing; requires declarations | dynamic typing |
| compiled | interpreted |
| explicit pointer variables and pointer operations | in-built list, set and dictionary structures and operations |
⚠️ GENERAL WARNINGS WHEN OPERATING THE CHAINSAW ⚠️
- don't always follow warnings blindly
- Eg.
if (x=1)will give a warning and ask you to make itif ((x=1))but it should beif (x==1)
- Eg.
PROGRAM STRUCTURE
/*
// (1) short description of program, author and date
# Description: Adds pi to a number
# Author: Cindy Chuah
# Date: 05/08/2021
*/
// (2) header file declarations:
#include <stdio.h>
// (3) global declarations
#define PI 3.1415
int main() {
// (4) local variable declaration:
int num;
// (5) statements
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
printf("%d + pi = %.2f", num, num+PI);
}
COMPILING AND EXECUTING
- Compiling Command:
gcc -Wall -ansi -o [filename] [filename.c] - Running Command:
./[filename]
COMMENTING
/*comment*/multi-line comments//commentsingle-line comment
PRINTING & INPUTTING
printf("format string", var1, var2)displays data (formats defined by the format string) as a string to the output stream- if successful, total number of characters written is returned
- on failure, a negative number is returned
- eg:
printf("I love %s%d", "COMP", 10002)
scanf("format string", &var1, &var2)receives input from keyboard&varaddress of a variable
Format String
- contains text to be written to stdout
Placeholder
- contain format tags to be replaced by the values specified in subsequent additional arguments and formatted as requested - aka placeholders
- Format tags:
%[flags][width][.precision][length]specifier - Specifiers
%ccharacter%dor%isigned (can be positive or negative) decimal integer%ffloat%lflong float%sstring of characters%ppointer
Control Characters
\nnew line\rcarriage return\"quotation mark\'apostrophe\\backslash
ASSIGNMENT/DECLARATION
#define [CONSTANT] [value]define a constant with value- type is automatically defined
variable = expressionassigns the expression to the variable
DATA TYPES
intinteger⚠️ Integer overflow and underflow
- $2^{31}-1=2,147,483,647$
#include <stdio.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int big, bp1, bt2, bp1t2; big = 2147483647; bp1 = big+1; // -2147483648 👈 bt2 = big*2; // -2 👈 bp1t2 = bp1*2; // 0 👈 /* 👈 = clearly not the correct answers due to iteger overflow yet, no warning it given by compiler */ printf("big=%d, bp1=%d, bt2=%d, bp1t2=%d\n", big, bp1, bt2, bp1t2); return 0; }- Fun fact: If Boeing 787 switched on for 248 days, the power shuts off and you fall out of the sky
- ⚠️ Integer division VS Double division
1/2 = 1(floor/integer division)1.0/2 = 0.5,1/2.0 = 0.5,1.0/2.0=0.5- you must 'infect' the calculation with a double for the result to be a double
strstring- Eg.
"string"
- Eg.
charcharacter- Eg.
'A'
- Eg.
longlong integerfloatfloat numberdoublelong float⚠️ floating point arithmetic and rounding error
- use doubles:
doublesstore approximate values over a much larger range thanintvariables
int main() { double d1, d2, d3; d1 = 0.1; d2 = d1 + d1 + d1 + d1 + d1 + d1 + d1 + d1 + d1 + d1; d3 = d2 - 1.0; printf("\n Doubles:\nd1 = %23.20lf\nd2 = %23.20lf\nd3 = %23.20lf\n", d1, d2, d3); float f1, f2, f3; f1 = 0.1; f2 = f1 + f1 + f1 + f1 + f1 + f1 + f1 + f1 + f1 + f1; f3 = f2 - 1.0; printf("\nFloats:\nf1 = %23.20f\nf2 = %23.20f\nf3 = %23.20f\n", f1, f2, f3); }RESULT: Doubles: d1 = 0.10000000000000000555 d2 = 0.99999999999999988898 d3 = -0.00000000000000011102 Floats: f1 = 0.10000000149011611938 f2 = 1.00000011920928955078 f3 = 0.00000011920928955078 THEREFORE, USE ALWAYS USE DOUBLES!!- use doubles:
⚠️ C does not have boolean type
zero (
0) is interpreted as falsenon-zero (
1,-23,87.9...) is interpreted as truedefining true and false:
// using #define #define true 1 #define false 0 // using const const int true = 1; const int false = 0
[object Object] vs [object Object]
char + intis validcharholds 4 bytesintholds 1 byte
OPERATORS (Highest to Lowest Precendence)
note: not every operator is here
- Precedence: Postfix -> Unary -> Multiplicative -> Additive -> Coparison/Relational -> Equality -> Logical AND -> Logical OR -> Assignment
- ⚠️ use parenthesis
()so you don't need to remember precedenceIncluding redundant parentheses costs nothing. Omitting necessary parentheses can cost
- Postfix
a++post-increment; same as a+=1a--post-decrement; same as a-=1
- Unary
!logical NOT!(!x) == xBUT, because C uses integers instead of booleans:- when x=5:
!(!x)=>!(!5)=>!(0)=>1, which is not x ;-;
-negative+positive(type)cast operator- converts objects to another type
- Multiplicative
*,/,%modulus- ⚠️ Cannot include doubles
19.0 % 4.0and19.0/4is illegal19/4is legal (result is equal to 3)
- ⚠️ Cannot include doubles
- Additive
+,-
- Comparison/Relational
<,>,<=,>=
- Equality
==,!=
- Logical AND
&&
- Logical OR
||
- Assignment
=,+=,-=,*=, ...
- ⚠️
&&and||go from left to rightif (LHS && RHS) {...}- if the LHS is false, RHS not evaluated
if (y && x/y) {...} // if y is 0, then x/y will not be evaluated // and you won't get a 'division by 0' error
- if the LHS is false, RHS not evaluated
if (LHS || RHS) {...}- if the LHS is true, RHS not evaluated
- other logical expressions: NOT NECCESARILY left to right
CONDITIONALS
[object Object]
if ([guard condition1]) {
// code to run if condition1 is true
} else if ([guard condition2]) {
// code to run if condition2 is true
} else {
// code to run if none of the above conditions are true
}
Example 1:
num_neg += (n<0)- same as
if (n<0) num_neg += 1;Example 2 (function exit):
/*checks if 3 (integer) inputs are received*/ if scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &r){ // scanf returns number of successfully valid inputs printf("scanf failed to read three items\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); }exit(EXIT_FAILURE)terminates program and signals an errorexit(EXIT_SUCCESS)terminates program without signaling an error
eqalinif.c- make sure you use
==to check for equality - not
=, which is used for assignment
- make sure you use
danglingelse.c- use explicit braces when nesting conditions
- compiler doesn't care about indentation
threetest.c(4 < 3 < 2)- will become
((4 < 3) < 2) - since 4 < 3 evaluates to 'true'
- the compiler will change the value of that to 1
- (because no booleans in C)
- the compiler will change the value of that to 1
- the statement will become:
(1 < 2) - which will evaluate to 'false' (aka 0)!
- will become
[object Object]
☠️ Don't use in assignments and exam
- never use switch lol
- can have different interpretations
switch (variable){
case ...1:
// code that runs if the variable is equal to ...1
break;
case ...2:
case ...3:
// code that runs if the variable is equal to ...2 or ...3
break;
default:
// 'else' code
break;
}
LOOPS
breakends loop immediatelycontinuemoves on to next iteration
[object Object] loops
for (initialize; guard; update) {
// statements
}
[object Object] loops
while (guard) {
// statements
}
// same as
for ( ;guard; ) { // no initialise and update
// statements
}
[object Object] loop
☠️ Don't use in assignments and exam
do {
// statements
}
while (guard)
[object Object] and [object Object]
getchar()returns the character readEOFmeans 'End of File' ('Enter' button)
putchar()prints the character returns the character written
FUNCTIONS
- provide a mechanism of abstraction
- simplify to steps
- code organisation
- easy to check that function-step is correct
- operations with multiple lines -> create a function
- each function should have a single function
- choose meaningful function names
- variables get deleted after function call finishes
- Limitation of functions: can only return 1 value with 1 type
// function signature/prototype
returnType functionName(type1 arg1, type2 arg2, ...);
// function call
functionName(arg1, arg2, ...);
// function definition
returnType functionName(type1 arg1, type2 arg2, ...) {
// statements
// return statement
return [expression];
}
- Example (Adding numbers):
#include <stdio.h>
int addNumbers(int a, int b); // function prototype
int main()
{
int n1,n2,sum;
printf("Enters two numbers: ");
scanf("%d %d",&n1,&n2);
sum = addNumbers(n1, n2); // function call
printf("sum = %d",sum);
return 0;
}
int addNumbers(int a, int b) // function definition
{
int result;
result = a+b;
return result; // return statement
}
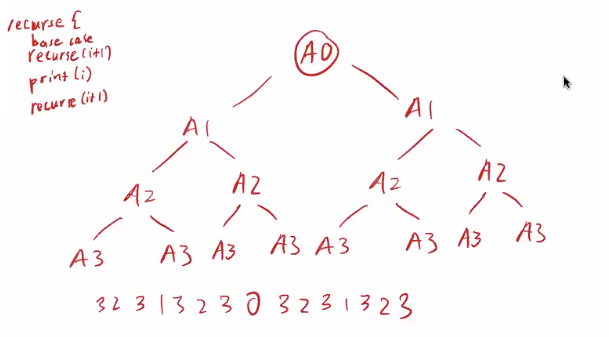
RECURSION
- 2 main parts
- base case: normally when the function calls should end
- recursive step: usually breaking down the problem into a smaller problem and an iterative step
/*Calculate the nth triangle number using recursion*/
int t_rec(int n) {
if (n==0) { // Base Case
return 0;
} else {
return n + t_rec(n-1); // Recursive Case (make sure to change n)
}
}
- statements before recursive call vs statements after recursive call
- recursion tree
Towers of Hanoi
- larger disks cannot be put on top of smaller disks
- optimal way to move disks from A to C
[object Object] LIBRARY
- Some functions
sin(x)log(x)fabs(x)floating point value of x
- constants
M_PIpiM_SQRT2square root of 2
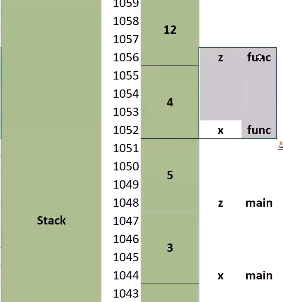
POINTERS
| address | value | variable |
|---|---|---|
| 1052 | 1048 | pointer |
| 1048 | 5 | var |
- special type of variable
int *pxpointer variable declaration- type of pointer can also be
void
- type of pointer can also be
px = &xstore address of x in pointer variable*pxreturns value in addressprintf("%d", *px) // prints value of x
pxreturns the address stored in px (aka address of x,&x)- Stack Oveflow
- an undesirable condition in which a particular computer program tries to use more memory space than the call stack has available
SCOPE
- scope heirarchy
- local variable -> local static variable/function arg variable -> global variable
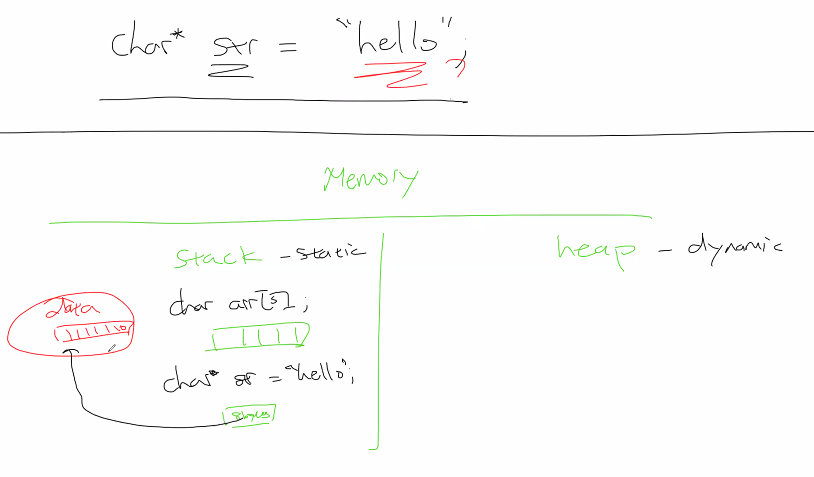
- global scope
- ❗ refrain from using global variables
- stored in data
- can be used in any function in the program
static [type] [var]modifier - only runs initialisation once - variable in function holds value- stored in data segment
- allow functions to maintain state from one call to the next without being accible to other functions
- Use case: counting number of times function was called
- local scope
- stored in stack
- declared inside functions
- can only be used within the function
- even if variable names are the same, a variable in a function does not affect and is not the same as a varibale in another function
int global; // stored in data
int func(int argvar);
int main() {
int mainlocal; // stored in stack (main is also a function)
...
}
int func(int argvar) {
int funclocal; // stored in stack
...
// funclocal -> static/argvar -> global
}
ARRAYS
- ❗ There is no execution-time array bounds checking, and responsibility rests with the programmer
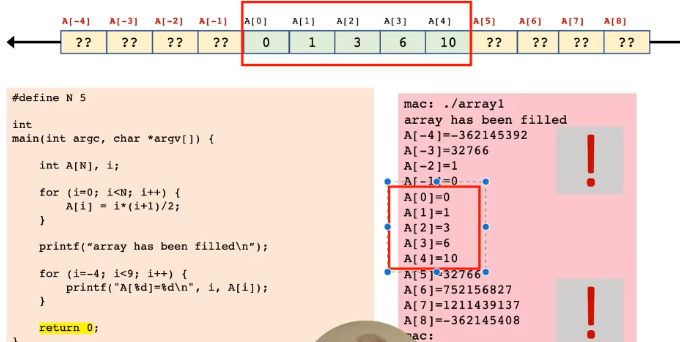
- "I must not use a value of
ithat is outside the range of the array"
- size of each element in array must be declared
- don't need to declare number of elements

#define N 5 // hash define for array size
int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {
int A[N]; // array declaration
// fill in array
for (int i = 0; i<N; i++) {
A[i] = i*(i+1)/2;
}
printf("array has been filled\n");
// print array
for (i=0; i<N; i++){
printf("A[%d]=%d\n", i, A[i]);
}
return 0;
}
A[n]an array of n variablesApointer constant- stores address of first variable in the array
&A[0]
- stores address of first variable in the array
- we can also use pointers to access arrays
- we can add/subtract pointers
int Y[5][10]2D array declaration- Y is an arary of 5 arrays of 10 ints
- when 2D arrays are passed to functions, only the dominant dimension can be left unspcified
func(A[][COLS])
- arrays can be initialized on declaration by supplying a list of values in braces
int arr[2] = {1, 2}
- always
#definearray sizes to avoid magic numbers
INSERTION SORT
void int_swap(int *num1, int *num2) {
int temp = *num1;
*num1 = *num2;
*num2 = temp;
}
void insertion_sort(int A[], int n) {
for (int i=1; i<n; i++) {
for (int j=i-1; j>=0; j--) {
if (A[j+1]<A[j]) {
int_swap(&A[j], &A[j+1]);
}
}
}
}
- best case: $O(n)$
- array already sorted
- worst case: $O(n^2)$
- average case: $O(n^2)$
SELECTION Sort
void int_swap(int *num1, int *num2) {
int temp = *num1;
*num1 = *num2;
*num2 = temp;
}
void selection_sort(int A[], int n) {
for (int i=n-1; i>0; i--){
// scan through array
int largest = 0;
int largest_index = 0;
int j;
for (j=0; j<=i; j++){
// found largest
if (A[j] > largest){
largest = A[j];
largest_index = j;
}
}
int_swap(&A[largest_index], &A[i]);
}
}
- best case: $O(n^2)$
- array already sorted
- worst case: $O(n^2)$
- array is soretd BUT the smallest element is the last element (eg. 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1)
- average case: $O(n^2)$
QUICKSORT
- divide and conquer algorithm
- using extreme elements as pivot element: $O(n^2)$
- best case: $O(n\log n)$
- partition process always picks the middle element as pivot
- worst case: $O(n^2)$
- partition process always picks extreme elements (smallest or largest) elements as pivot
- average case: $O(n\log n)$
Proving Correctness
 ...
...
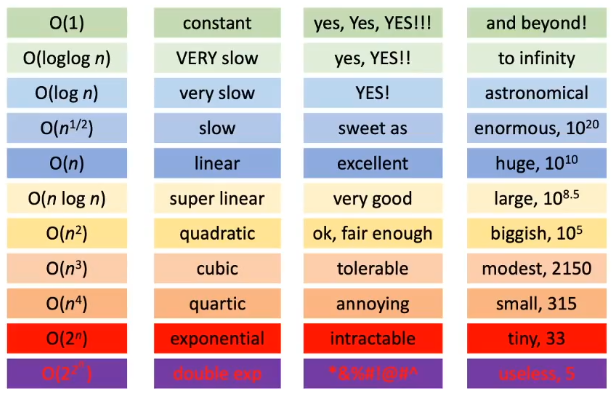
BIG O
ALGORITHMS
- heart of computing
Correctness
- assertions: argued statements about what must be true as a program executes
- with the use of logic, and precise rules associated with the semantics of executable statements, invariants can be used to provide formal proofs of program correctness
- Example: Linear Search


Pis loop invariantassert(...)pseudo-function to do your own array bounds checking
Efficiency
- memory space required
- execution time
- Example: Linear Search
- best case: item x found in first location
- worst case: item notfound
- n loop iterations required
LINEAR SEARCH
- unsorted
- sorted
- still
O(n)
- still
BINARY SEARCH
- only for sorted array
- Invariant


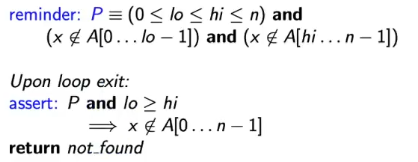
- important to demonstrate that loops terminate
/* recursive binary search
*/
int binary_search(data_t A[], int lo, int hi, data_t *key, int *locn){
int mid, outcome;
if (lo >= hi) {
return BS_NOT_FONUD;
}
mid = (lo+hi)/2;
if ((outcome = cmp(key, A+mid)) < 0) {
return binary_search(A, lo, mid, key, locn);
} else if (outcome > 0) {
return binary_search(A, mid+1, hi, key, locn);
} else {
*locn = mid;
return BS_FOUND;
}
}
cmp(A, B)comparison function- usually passed into sorting/searching functions as a function argument
- compares two elements
AandB - returns:
-veifAcomes beforeB0ifAandBare equal+veifAcome afterB
- Time Complexity:
O(log n)
[object Object]
- another layer of abstraction
#define SIZE 5
typedef double vector_t[SIZE]
typedef vector_t sqmatrix_t[SIZE]
int main() {
vector_t A, B;
// A and B are vectors of 5 doubles
sqmatrix_t C;
// C is a vector of 5 vectors of 5 doubles
}
STRINGS
- array of type
char// character pointer include <string.h>'\0'null byte - signifies end of stringchar str1[10] = {'h', 'i', '\0'}char str1[11] = "helloworld"orchar *p = "Hello World- adds nullbyte implicitly
- array must have enough space for nullbyte
- printf/scanf using
%sprintf("%s", str1)`scanf("%s", str2)- don't need
&because the string is a pointer - implicitly adds null-byte at the end
- don't need
strlen(char *str1)returns length of stringstrcpy(char *dest, char *src)copies string from src_str to dex_strstrncpy(char *dest, char *src, int n)copiesncharacters from src to destdestmust be at least n bytes long
strcmp(char *str1, char *str2)for comparing strings- we cannot use
==because comparing pointers (address)
- we cannot use
strncmp(char *str1, char *str2)compares n characters in str1 and str2strcat(char *dest, char *src)appends a copy of src to dest by overwriting its null bytedestmust be large enough to acoommodate the extended string- Risky
strncat(char *dest, char *src, int n)copies n characters from src to the end of dest, replacing its null-byteatoi(char *s)returns the integer value represented by the characters ofsatof(char *s)returns the double value represented by the character ofsisalpha()returns 1 if character is an alphabetical character and 0 otherwise
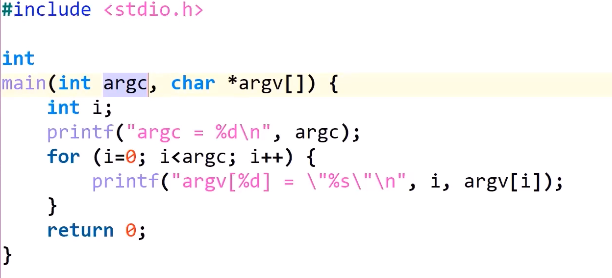
[object Object]
- allows us to store comand line arguments
char* argv[]- array of pointers (that point to strings)

- cannot access when declared in data
- why useful
- reading files
- more input ways
PATTERN-MATCHING ALGORITHMS
- Given: A text sequence
T[0 ... n-1]and a patternP[0 ... m-1] - Question: Does pattern P appear as a continuous subsequence of text T? If so, where?
Sequential pattern search
void naive_search(char* T, char* P) {
int n = strlen(T);
int m = strlen(P);
int found = FALSE;
int s=0;
while (s <= n-m) {
int i;
for (i=0; i<m; i++){
if (T[s+i] != P[i]){
break;
}
}
if (i == m){
printf("Found at %d\n", s);
found = TRUE;
}
s++;
}
if (!found) {
printf("Not Found\n");
}
}
- Best Case:
O(n)- first character in pattern is not in text
- Text:
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa - Pattern:
baa
- Worst Case:
O(nm)- last character in pattern is not in text
- Text:
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa - Pattern:
aaab
- Average Case:
O(n)
Knuth-Morris-Pratt (KMP) Search
- ❗ in exam
- understand how it works - don't memorise the code
- Problem: Find substring in text
- does "aab" occur in "aaacabaabaa"
- Brute Force
- compare substring at every index in the text
- time complexity: $O(mn)$
- m = length of substring
- n = length of text
- Knuth-Morris-Pratt KMP search
- if mismatch occurs, shift the pattern forward as far as possible without moving past any matching prefix of the pattern
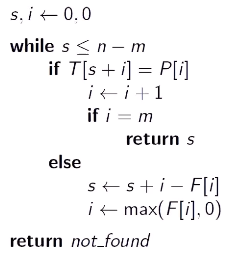
- Failure Array
- Define
F[i]to be the maximum k<i such thatP[0 ... k-1]matchesP[i-k ... i-1], withF[0]set to be -1 - At each mismatch, can shift
Pright byi(mismatch position) minus F[i] (allowance for pattern self-overlap) - If
F[i]is zero, then pattern search resumes from mismatched locations+i, rather thans+1 
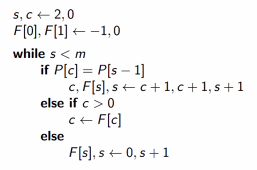
- how to find failure array:
- first 2 elements:
[-1, 0] - "How many suffix is also a prefix?"
- other elements are
0
- first 2 elements:
- Average less than
O(2m)
- Define
- Average case
O(m + n)- generally,
O(m+n) < O(2m) - because
m <= n
- generally,
Boyer-Moore Horspool (BMH) Search
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/boyer-moore-algorithm-for-pattern-searching/
- best case:
O(n / m) - worst case:
- average case:
O(n)
Suffix Array
- generate
nsuffix strings of text - sort these suffix string
- using ternary quicksort
- build time:
O(n^2 log(n)) - search in suffix array:
O(m log(n))m << n
- why declare a suffix array (when the build time is bigger)?
- amortize complexity
- which operation is used the most?
- searching
- which operation is used the most?
- building is only done once * can be pre-computed

- amortize complexity
KMP Search VS BMH Search
- KMP
- skip comparisons based on comparisons that we have alread done
- suffixes that are prefixes
- skip comparisons based on comparisons that we have alread done
- BMH
- comparing starting at the end of the substring
- assuming that if we don't get a match at the end, we don't need to compare at the start

Structs

- struct names end with
_t
// struct for storing date of births
typedef struct {
int day;
int month;
int year;
} dob_t;
// create a profile struct for storing student profiles
struct profile {
char name[20];
int age;
int student_id;
dob_t dob;
}
typedef struct profile profile_t;
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// create an instance of the struct
profile_t student;
// setting int values
student.age = 21;
student.student_id = 321456;
// setting string values
strcpy(student.name, "Jane")
}
- has component name
student.age = 21strcpy(var.student, "Jane")- Arrays VS Structures
- structures: can store different types
- arrays: storing different instances of the same type
- arrays: assuming that every element is independent of each other
- eg. date - should be struct, even though they are all
int
- structures get copied
profile_t temp = var; // var is a copy of profile_t temp.age = 100; // only temp's age student->age = 32dereferencing and accessing - to change value of variable using functions- same as
(*student).age = 32
- same as
Dynamic Memory
size_t sizeof(thing)returns the number of bytes required to store the type or variablething- not really a function
malloc()dynamically declares arraysint* array = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 10)dynamically declares 10 ints into an arrayusing malloc in function - array doesn't get destroyed (even though it's local):
int* give array() { int* array = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 10); assert(array) return array; }
realloc()
array = (int*)realloc(array, sizeof(int) * 20)changes size of arrayO(n)time complexity
// read in num_rows
big_arr = malloc(sizeof(int) * num_rows)
for (int i=0; i<num_rows; i++){
}
QUIZ 2
- string functions
- type compatibility
- ✅ pointer + string/character
- ❌ pointer + pointer
Structs VS Arrays
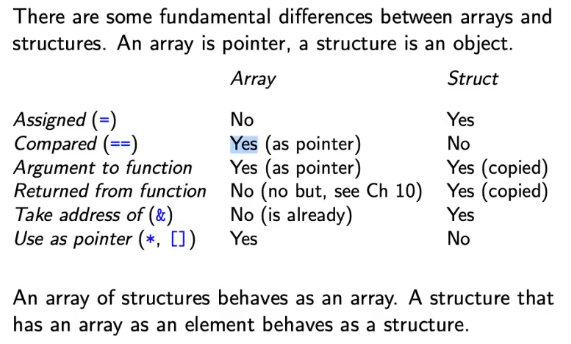
Assigned (
=)- Array: No
B=Adoes not copy the array
- Array: No
Compared (
==)Argument to function
Returned to function
Take address of (
&)Use as pointer (
*,[])doublehas alignment requirement- has to start on multiple of 8
Linked Lists
node1 (head) node2 node3 (foot)
+------+------+ +------+------+ +------+------+
| data | next | --> | data | next | --> | data | next |
+------+------+ +------+------+ +------+------+
#include <assert.h>
typedef struct node node_t
struct node {
int data;
node_t* next;
}
node_t* make_new_node(int data);
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
// Declare a local linked list
node_t* head = NULL;
node_t* tail = NULL;
int input;
while(scanf("%d), &input) == 1) {
// Want to make a node
}
}
node_t* make_new_node(int data) {
node_t* newnode = (node_t*)malloc(sizeof(node_t))
assert(newnode)
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
Make a new node
Appending to head
- malloc a new node
- make new node point to head
- change the head to be the new node
Appending to tail
- malloc a new node
- make tail point to new node
- change the tail to be the new node
Append in between
- make temp traverse through linked list
- newnode->next = temp->next
Binary Search Trees
- Worst case: Stick
int is_stick(node_t* root){ if (root->left && root->right) { return FALSE; } if (!root->left || !root->right) return is_stick(root->left) && is_stick(root_right); } - use recursion
- In-order traversal
void traverse(root) { if (root) { traverse(root->left); printf(root->data); traverse(root->right); } } - Pre-order traversal
- used for copying trees
void traverse(root) { if (root) { printf(root->data); traverse(root->left); traverse(root->right); } } - Post-order traversal
- used for deleting/freeing trees
void traverse(root) { if (root) { traverse(root->left); traverse(root->right); printf(root->data); } }
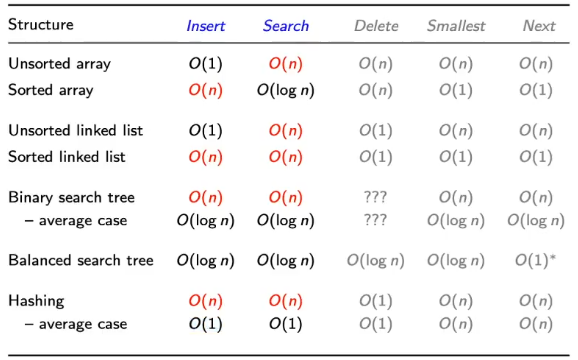
Arrays, LInked Lists and BST Summary
| Operation | Array(unsorted) | Linked List(unsorted) | Array(sorted) | BST(balanced) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Search | $O(n)$ | $O(n)$ | $O(\log n)$ | $O(\log n)$ |
| Insert | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$(to head)<br>$O(n)$(to tail) | $O(n)$ | $O(\log n)$ |
| Remove | $O(n)$ | $O(n)$ | $O(n)$ | $O(\log n)$ |
Number Representations
Two's Complement Integers
File Operations
- in
<stdio.h> - 3 files that are always provided when a program is executing:
stdininput from keyboard; can be redirected using<printf(...)is a call tofprintf(stdout, ...)
stdoutoutput to screen; can be redirected using>scanf(...)is a call tofscanf(stdin, ...)
stderrerror output- generated using
fprintf(stderr, "xx", yy)
- generated using
FILE* filepointerdeclaring filepointersfopen(const char *filename, const char *mode)returns file pointer to the opened filefilenamestring containing name of file to be opened (please #define this)modeaccess mode string:"r"open for reading"w"creates empty file for writing. If file already exists, previous contants deleted at moment of opening"a"open for appending, previous contents retained"r+"open for reading and writing"w+"creates empty file for reading and writing"a+"opens file for reading and appending
freopen(const char*filename, const char *mode, FILE *stream)return pointer to an object identifying the stream, if file oe-opened successfully - otherwise, null pointer is returnedfilenameandmodesame asfopen(...)streampointer to FILE object that identifies stream to be re-opened
fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmenb, FILE *stream)returns total number of elements successfully readptrpointer to the array of elements to be readsizesize in bytes of each element to be readnmembnumber of elements, each one with a size ofsizebytesstreampointer to a FILE object that specifies an input stream
fwrite(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream)returns total number of elements successfull writtenptrpointer to the array of elements to be writtensizesize in bytes of each element to be writtennmembnumber of elements, each one with a size ofsizebytesstreampointer to a FILE object that specifies an output stream
fclose()close a file
/* Writing to a text file */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int num;
FILE *fptr;
// use appropriate location if you are using MacOS or Linux
fptr = fopen("C:\\program.txt","w");
if(fptr == NULL)
{
printf("Error!");
exit(1);
}
printf("Enter num: ");
scanf("%d",&num);
fprintf(fptr,"%d",num);
fclose(fptr);
return 0;
}
/* Reading from a text file */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int num;
FILE *fptr;
if ((fptr = fopen("C:\\program.txt","r")) == NULL){
printf("Error! opening file");
// Program exits if the file pointer returns NULL.
exit(1);
}
fscanf(fptr,"%d", &num);
printf("Value of n=%d", num);
fclose(fptr);
return 0;
}
Floating Point Numbers (IEEE754)
Algorithm
- Convert the decimal into binary
- eg. 14.25 -> 1110.01
14 = 8 + 4 + 2 + 00.25 = 0*1/2 + 1*1/4
- eg. 14.25 -> 1110.01
- Convert the binary number to
1.xxx... * 2^(pow)- eg.
1.11001 * 2^3- moved decimal point 3 to the left
- eg.
- Mantissa:
xxx...- eg.
11010000...000(until 23bits)
- eg.
- Exponent:
pow + constin base 2const: 127 for 32-bit- eg.
3 + 127 = 130 -> 10000010
- Sign bit is either
+veor-ve- eg. 32-bit floating point num:
0 10000010 11001000...000
- eg. 32-bit floating point num:
- Convert the decimal into binary
32-bit floating point Numbers
1 bit 8 bits 23 bits sign exponent mantissa - bits can be different in exam
Octal
- base 8 (2^3)
- 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
Hexadecimal
- base 16 (2^4)
- 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, a, b, c, d, e, f
Monte Carlo Methods
- Use pseudo-random number generation to allow modeling of a physical system
srand()initialize random-number sequencerand()returns next seemingly-unrelatedintin the sequence
Stack
- LIFO: Last in, First out
- Operations to be supported
S <- stack_create_empty()stack_is_empty(S)S' <- stack_push(S, item)item <- stack_top(S)S' <- stack_pop(S)
- Implementation Options: Array (with realloc), Linked List
- All operations should take
O(1)time
typedef struct {
int *arr;
size_t count, max_size;
} stack_t;
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#define STACK_SIZE 10
typedef struct {
int *arr;
size_t count, max_size;
} stack_t;
stack_t *create_empty_stack(void) {
stack_t *s = (stack_t *) malloc(sizeof(stack_t));
s->arr = (int *)malloc(STACK_SIZE*sizeof(int));
assert(s && s->arr);
s->count = 0;
s->max_size = STACK_SIZE;
return s;
}
void recursive_print(stack_t *stack, size_t depth) {
}
Queue
- FIFO: First In First Out
- Operations to be supported
Q <- queue_create_empty()queue_is_empty()Q' <- queue_append(Q, item)item <- queue_head(Q)Q' <- queue_tail(Q)
- Implementation options: Circular Array, Linked List
- All operations should take
O(1)time
Priority Queue
- Operations to be supported:
Q <- pq_create_empty()pq_is_empty(Q)Q' <- pq_insert(Q, item, priority)item <- pq_max_priority(Q)Q' <- pq_delete_max(Q)
- Implementation options:
- Operation Cost:
Dictionary
- Operations to be supported
D <- dict_create_empty()dict_is_empty(D)D' <- dict_insert(D, item, key)item <- dict_search(D, key)D' <- dict_delete_item(D, key)
- plus(maybe):
item <- dict_smallest(D)item' <- dict_next_element(D, item)
- Implementation options

Hashing
- Hashing Function,
h(): deterministically construct a semmingly-random integer- depends on initial
seedso it is reusable - never just add character values or shift-n-add -- not enough randomness
- depends on initial
- Collisions: when different values get same hash value
- Birthday Paradox: In a room of 23 people, there is a 50-50 chance of at least 2 people habing the same birthday
- Buckets
- use linked lists
Mergesort
mergesort(A[0...n-1])
if n<=1
// already sorted
return
// [1] split into 2 parts
mid = n/2
// [2] recursively sort each part
mergesort(A[0...mid-1]) // sort first half
mergesort(A[mid...n-1]) // sort second half
merge(A[0...mid-1], A[mid...n-1])
- Divide-and-conquer
- Difference with Quicksort:
- Quicksort: "Hard split, easy join"
- Mergesort: "Easy split, hard join"
- split into 2 parts
void merge_sort(data_t A[], int n) { data_t *T; T = malloc((n/2)*sizeof(*T)); assert(T != NULL); recursive_merge_sort(A, n, T); free(T); } - recursive call: to sort each part
static void recursive_merge_sort(data_t A[], int n, data_t T[]) { int mid; if (n<=1) { return; } mid = n/2; recursive_merge_sort(A, mid, T); recursive_merge_sort(A+mid, n-mid, T); merge(A, mid, n, T); } - merge
static void merge(data_t A[], int mid, int n, data_t T[]) { /* merge array sections A[0..mid-1] and A[mid..n-1] */ int i, s1, s2; /* copy first section into temporary array T */ for (i=0; i<mid; i++) { copy_data(T+i, A+i); } i = 0; s1 = 0; s2 = mid; /* merge second section at A[mid] with T, putting output back into section starting at A[0] */ while (s1<mid && s2<n) { if (cmp(T+s1,A+s2) < 0) { /* element from T goes next */ copy_data(A+i, T+s1); s1 += 1; } else { /* element from A goes next */ copy_data(A+i, A+s2); s2 += 1; } i += 1; } while (s1<mid) { /* copy over any remaining elements in T */ copy_data(A+i, T+s1); s1 += 1; i += 1; } /* all elements are now in their final positions */ }
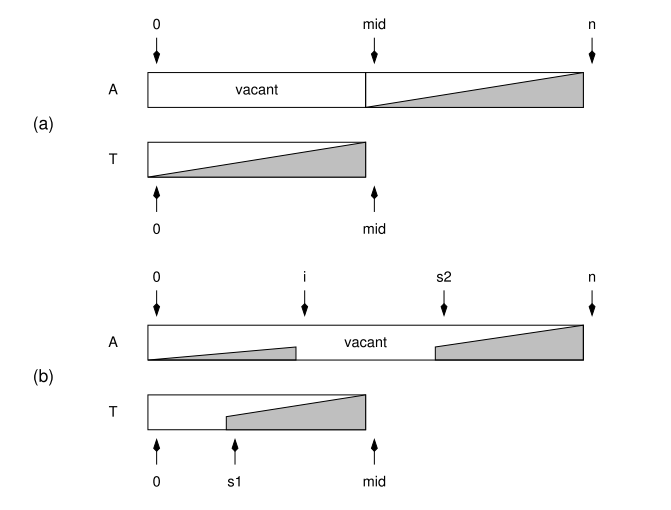
- Worst case: $O(nlog n)$
- Cons: takes extra space

Heapsort
- Create an implicitly balanced tree based on array positions
- array: A[0...n-1]
- for item
A[i]- children:
A[2i+1]andA[2i+2] - parent:
A[(i-1)/2]
- children:
- Make it a heap
- Rule: no child may be larger than its parent
A[i] <= A[(i-1)/2]
void sift_down(data_t A[], int parent, int n) { int child; if ((child = 2*parent+1) < n) { /* there is at least one child to be checked */ if (child+1<n && cmp(A+child, A+child+1)<0) { /* the right child exists, and is larger */ child += 1; } if (cmp(A+parent, A+child)<0) { /* parent is smaller than larger child */ swap_data(A+parent, A+child); sift_down(A, child, n); } } } void build_heap(data_t A[], int n) { int i; for (i=n/2-1; i>=0; i--) { sift_down(A, i, n); } }
- Heapsort
void heap_sort(data_t A[], int n) { int active; build_heap(A, n); for (active=n-1; active>0; active--) { swap_data(A+0, A+active); sift_down(A, 0, active); } }
- best case: $O(n\log n)$
- worst case: $O(n^2)$
- average case: $O(n\log n)$
- Pro: No extra space required