1 What are Database Systems?
Data vs Information
| Data | Information |
|---|---|
| known facts stored and recorded. | Data presented in context (can be summarised data). |
| text, numbers, dates, images, video, sound, etc | Processed and more useful |
Metadata
- data about data
- can include
- constraints
- rules
- structure
- Why we need it - to give data
- consistency
- meaning
- We generate a data dictionary as part of the analysis of system requirements
Database
- a large, integrated, structured collection of data
- usually intended to model some real-world enterprise
Database Management System (DBMS)
- software designed to…
- store
- manage
- facilitate access to
- …databases
DBMS vs File Processing Systems
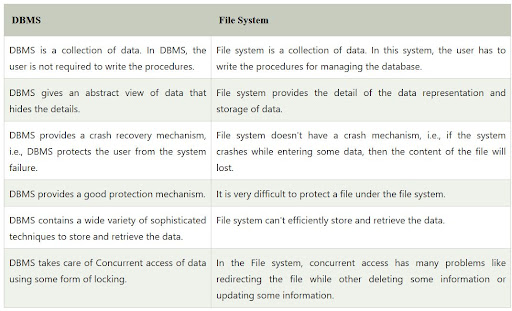
| Disadvantages of File Processing | Advantages of DBMS |
|---|---|
| Program-Data Dependence | Data Independence |
| Duplication of data | Minimal data redundancy |
| Limited data sharing | Improved data sharing |
| Lengthy development times | Reduced Program maintenance |
| Excessive program maintenance | Reduced Program maintenance |
| Hard to create adhoc reports | Easy to create adhoc reports |
| Security | Data integrity and security |
Program-Data Dependence
- if the file structure changes, so does the program
- what if you change data structure for one program
Data Independence
- Application programs should not, ideally, be exposed to details of data representation and storage. The DBMS provides an abstract view of the data that hides such details
Duplication of data
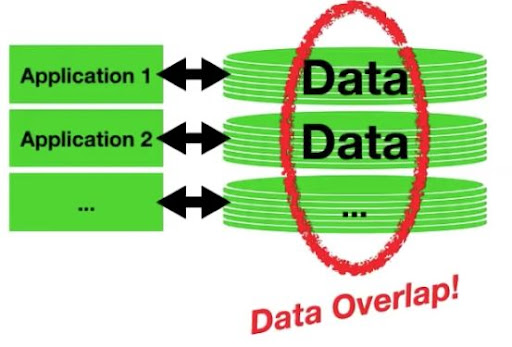
- wasteful, inefficient, loss of data integrity
Minimal data redundancy
- redundancy can be controlled through a process called normalization
Limited data sharing
- if a company uses a file processing system then that system has to be individually shared with people who want to view it, and each shared copy has to be individually updated when something in the system is changed
Lengthy development times
- slower to have to use your own custom code to
- open files
- parse them into useable data
- create some interface to access the parts of the file that are relevant
- manage concurrency
- backup the data
- allow for rollbacks etc. (all of the fancy things that DBMS can do, you’d have to replicate that all yourself!)
- slower to have to use your own custom code to
Improved data consistency
- single store: no disagreements, updata problems, less storage space
Excessive program maintenance
- up to 80% of development time in traditional file based organisations is for maintenance
Reduced program maintenance
- data structure can change without application data changing
Hard to create adhoc reports
- data tied to application, hard/slow to create adhoc reports
Easy to create adhoc reports
- Novel ad hoc data access ‘without programming’ using SQL
Security
- Operating system provides only a password mechanism for security
- This is not sufficiently flexible to enforce security policies in which different users have permission to access different subsets of the data
Data integrity and security
- if data is always accessed through the DBMS, the DBMS can enforce integrity constraints
- for example, before inserting salary information for an employee, the DBMS can check that the department budget is not exceeded
- also, it can enforce access controls that govern what data is visible to different classes of users
2 Database Development Process
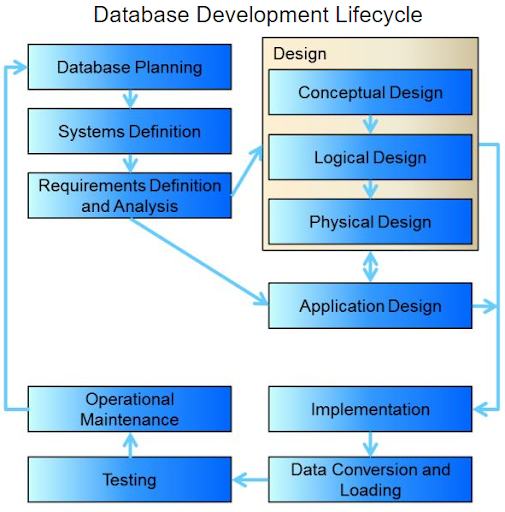
1 Database Planning
- Planning how to do the project
- How does the enterprise work
- Enterprise data model
- top level perspective on data requirements
- each box would have a data model
2 Systems Definition
🏗️ ...Work in Progress... 👷♀️