Coming Up
- Writing nice code
- Dictionaries
- Sets
Noneandsort()vs.sorted()
Writing Nice Code
Notes on Writing Nice Code
- ✅ Do
- Be clear and efficient
- Write scalable code
- think "can this code support bigger inputs?"
- Use loops
- Abstraction
- ❌ Don't
- Have lots of repetition
Problem 1
Do the following code snippets do the same thing? What are some advantages and disadvantages of each snippet? What if we needed a hundred different types of tool?
Example A:
print("We need some saws")
print("We need some hammers")
print("We need some cogs")
print("We need some nails")
Example B:
def get_str(part):
return f"We need some {part}"
print(get_str("saws"))
print(get_str("hammers"))
print(get_str("cogs"))
print(get_str("nails"))
Example C:
def get_str(part):
return f"We need some {part}"
parts = ("saws", "hammers", "cogs", "nails")
for part in parts:
print(get_str(part))
Problem 2
Consider the following while loop and two conversions to for loops. Are the two for loops equivalent? Why might you choose one over the other?
Original While Loop:
count = 0
items = ('eggs', 'spam', 'more eggs')
while count < len(items):
print(f"we need to buy more {items[count]}")
count += 1
For Loop A:
items = ('eggs', 'spam', 'more eggs')
for count in range(len(items)):
print(f"we need to buy more {items[count]}")
For Loop B:
items = ('eggs', 'spam', 'more eggs')
for item in items:
print(f"we need to buy more {item}")
Discussion 1
Dictionary Operations
Notes on Dictionary Operations
- Accessing
d[key]access value associated to key - returnsKeyErrorif key doesn't existd.get(key)returns value associated with key - returnsNoneif key doesn't existkey in dtest for presence of key
- Adding
d[new_key] = new_valueadding a new keyd.copy()makes a shallow copy of dictionary
- Deleting
d.pop(key)deletes key-value pairdel d[key]deletes key-value paird.clear()deletes all key-value pairs from the dictionary
- Iterables
d.keys()returns iterable collection of keysd.values()returns iterable collection of valuesd.items()returns iterable collection of 2-tuples (key, value)list(d)same aslist(d.keys())
d = {
"name": "Jane",
"hobbies": ["coding", "basketball"]
}
print(f"Original dictionary: {d}\n")
print(list(d.items())[0])
for item in d.items():
print(item)
# # adding a new key
# d["age"] = 30
# print(f"After adding new key: {d}\n")
# # updating existing key
# d["name"] = "Alex"
# d["hobbies"].append("reading")
# print(f"After updating: {d}\n")
# # deleting
# pop_return = d.pop("hobbies")
# print(f'pop_return: {pop_return}')
# del d["name"]
# print(f"After deletions: {d}")
Discussion 2
What is the difference between using the .pop() method on a dictionary and using it on a list?
Sets
Notes on Set Operations
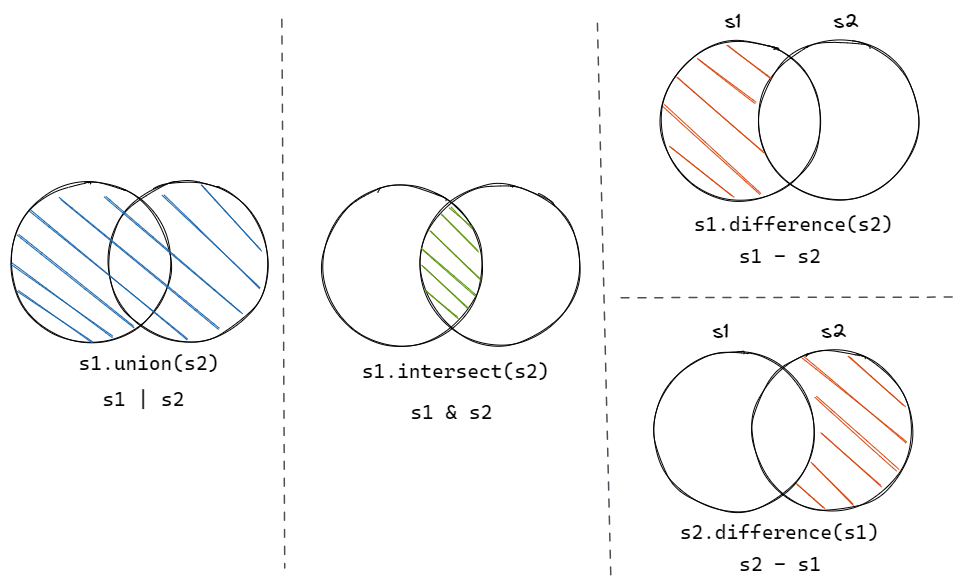
Discussion 3
In what situations would we use a “set”? How does it differ from other “containers” such as lists and dictionaries?
Discussion 4
What special operations can we perform on sets? How do we add and remove items from them?
Exercise 3
Evaluate the following given the assignment d = {"R": 0, "G": 255, "B": 0, "other": {"opacity": 0.6}}. Specify whether the value of d changes as a result. Assume d is reset to its original value each time.
(a) "R"in d
(b) d["R"]
(c) d["R"] = 255
(d) d["A"]
(e) d["A"] = 50
(f) d.pop("G")
(g) d["other"]["blur"] = 0.1
(h) d.items()
Exercise 4
Evaluate the following given the assignment s1 = {1, 2, 4} and s2 = {3, 4, 5}. If s1 or s2 change as a result, give their new value. Assume s1 and s2 are reset to their original values each time.
(a) s1.add(7)
(b) s1.add(2)
(c) s2.remove(5)
(d) s1 & s2
(e) s1.union(s2)
(f) s1 - s2
Problem 1
Write a function which takes a string as input and prints the frequency of each character in the string using a dictionary. freq_counts('booboo') should print:
b 2
o 4
Problem 2
Write a function which takes two lists as input and returns a list containing the numbers which they both have in common. in_common([1, 2, 4], [3, 4, 5]) should return [4].
Problem 3
Write a function which takes a dictionary and returns a sorted list containing the unique values in that dictionary. unique_values({'a': 1, 'b': 0, 'c': 0}) should return [0, 1].
Problem 4
Write a function which takes a string, a character and an integer threshold and returns True if the character appears in the string with a frequency above the threshold, False if it appears at or below the threshold, and None if it doesn’t appear at all. above_thresh('I like the letter e', 'e', 3) should return True.