Summary of Lecture Content
What is sound? Sound is energy in longitudinal waves, traveling through various mediums with attributes like amplitude (loudness), frequency (pitch), and wave shape (timbre).
Introduction to Recording Sound can be converted into electrical signals using microphones, analog or digital technology. Key components include ADC, DAC, and master clocks. The transition from physical to digital recording has boosted accessibility but demands expertise.
MP3 Revolution Positives: Enhanced music accessibility, easier sharing. Negatives: Intellectual property concerns, piracy. Cultural shifts like peer-to-peer sharing and streaming services impact professional production.
Audio Tools DAWs, microphones (condenser, dynamic, ribbon), and audio interfaces are crucial for recording and production.
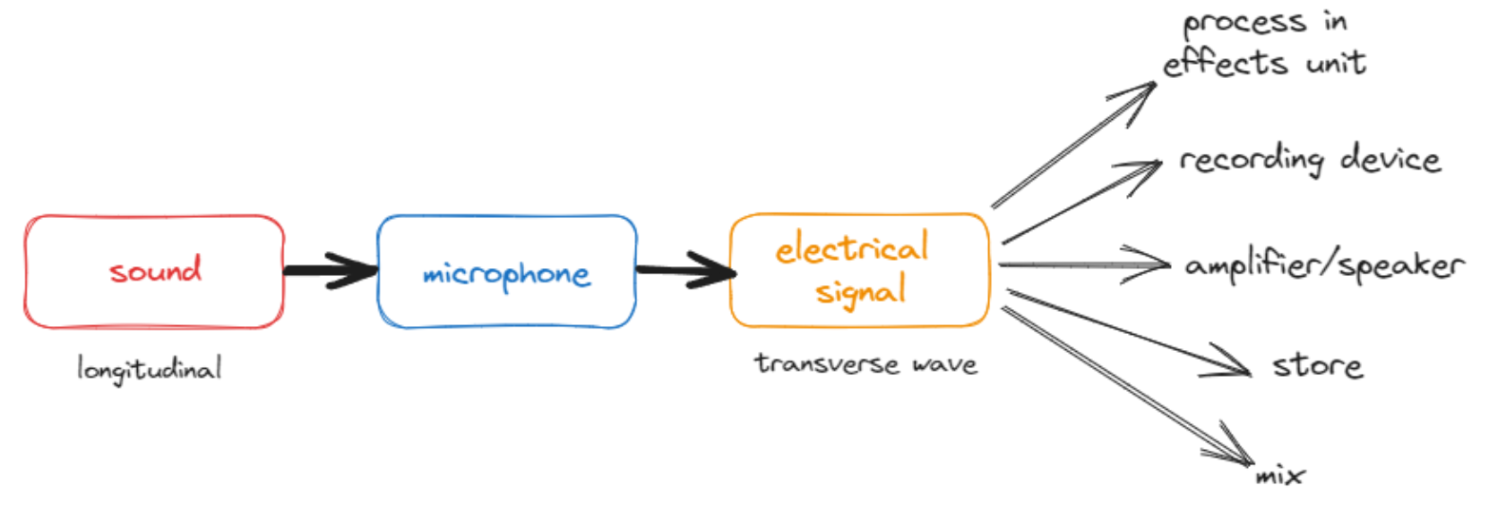
- How sound is converted from longitudinal to transverse waves in a microphone.
Professional Production Challenges The expectation of free content may threaten the sustainability of the recording industry and the livelihood of artists and creators.